Bulimia Nervosa (Eating Disorder) – Symptoms, Causes, And Treatments
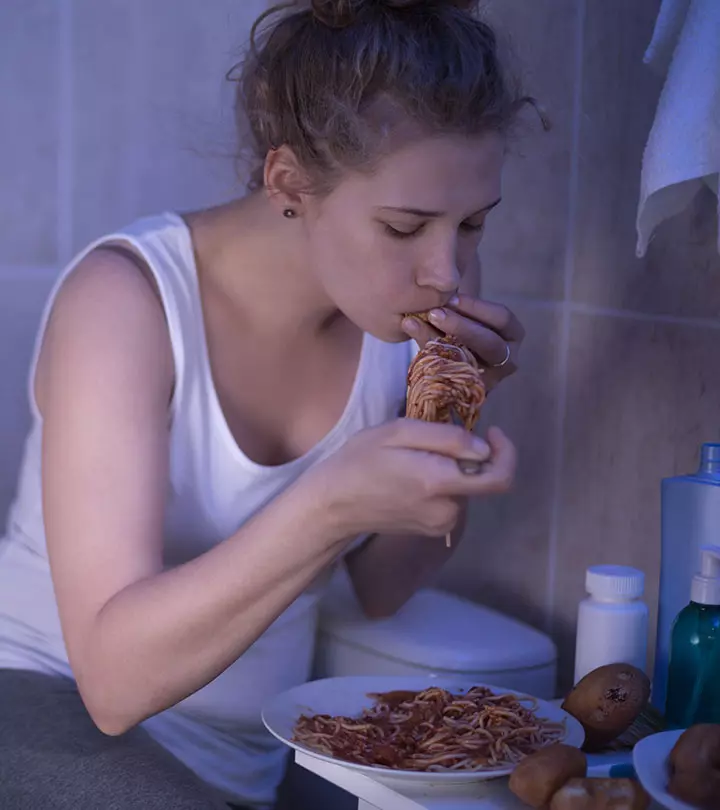

Image: Shutterstock
Bulimia nervosa is believed to affect 0.5% to 1% of young women, according to a community-based study (1).
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder. It causes the affected individual to binge eat and then exercise excessively or induce vomiting to make up for the extra calories. This disorder is usually a result of an underlying psychotic issue and may sometimes even be life-threatening if left untreated for too long. To know more about bulimia and the medical options to treat it, keep reading.
Table Of Contents
- What Is Bulimia Nervosa?
- Types Of Bulimia
- Signs And Symptoms
- Causes And Risk Factors
- Anorexia Nervosa Vs. Bulimia Nervosa
- Diagnosis
- Treatment Methods
- Best Diet Plan For Bulimia Nervosa
- Prevention Tips
What Is Bulimia Nervosa?
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder. It is a serious psychiatric illness that is potentially life-threatening. Bulimia nervosa is also referred to as bulimia. Those who have this disorder tend to binge eat and then make up for it by either over-exercising and purging, either by puking or using laxatives.
Bingeing involves eating large amounts of foods high in calories in a short period, usually in two hours. The concerned individual may consume 3000 calories or more. Once this behavior starts, it is hard to stop and cannot be controlled.
Post bingeing, an individual may feel bloated, guilty, and unattractive – all at the same time. Also, there is a looming fear of gaining weight. This fear leads to actions like self-induced vomiting, over-exercising, dieting, and overusing diuretics and laxatives. Purging often leads to serious complications and may even contribute to weight gain in the long run.
Bulimia is categorized into two types.
Types Of Bulimia
- Purging Type – This type accounts for a majority of the cases of bulimia. It is characterized by self-induced vomiting or abuse of laxatives, diuretics, and enemas in an attempt to lose weight after binge eating.
- Non-Purging Type – This type of bulimia is characterized by inappropriate actions of over-exercising or excessive fasting after a period of bingeing.
An individual with bulimia nervosa is usually of normal weight or could be slightly on the heavier side. The following are some symptoms that are behavioral indicators of bulimia.
Signs And Symptoms
The signs and symptoms associated with bulimia are (2):
- Eating alone always
- Sudden disappearance of food from the plate
- An obsession with food
- A lot of money spent on food alone
- Leaving the room soon after eating, usually to the washroom
- Hoarding or hiding food to eat later
- Excessive exercising
- Complaining about weight gain constantly
- Phases of fasting followed by binge eating
You may also notice laxatives or diuretics that are hidden away to induce purging.
The physical symptoms that may surface with purging are (3):
- Dehydration
- Nutrient deficiency
- Changing body weight
- Scars on the knuckles (also referred to as Russell’s sign) that result from fingers being forced down the throat to induce puking
- Acid reflux
- An inflamed throat
- Chronic sores
- Damaged teeth
- Swollen cheeks
- Irregular periods
- Appearance of broken blood vessels in the eyes
Symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression are also not uncommon in individuals who have bulimia. However, it could be difficult to identify these symptoms as bulimic individuals often try and hide them.
The affected individuals display unusual eating behavior to handle the emotional stress related to unwanted weight gain. They may be facing other challenges too that could be contributing to the development of bulimia. Listed below are some of the major factors that could be responsible for the onset of bulimia.
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors?
While the exact cause of bulimia remains unidentified, researchers are of the opinion that a combination of the following factors could be responsible for triggering it (4).
- Genetics – A family history of the condition
- Psychological factors – The fear of gaining weight
- Medical conditions like depression, anxiety, stress, and personality disorders
- Hormonal changes
- Parenting problems
- A history of being bullied
- Environmental factors like exposure to unhelpful role models via the media and fashion industry
- An early pregnancy
All these factors can trigger bulimia and/or may also increase an individual’s risk of developing it.
Many confuse bulimia nervosa with anorexia nervosa, which is also an eating disorder but with different symptoms. The following section lists the major differences between the two.
Anorexia Nervosa Vs. Bulimia Nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa
- This disorder surfaces from a distorted body image that may be due to depression, anxiety, or emotional trauma.
- Its symptoms include skipping meals or unhealthy dieting.
- Those who have anorexia are usually underweight.
Bulimia Nervosa
- It is an eating disorder that may be the result of underlying emotional trauma.
- Its symptoms include eating too much and then over-exercising or purging to make up for binge eating.
- Those who have bulimia usually weigh normal or may be slightly on the heavier side.
If you doubt that you or anybody you know could be dealing with life-threatening eating disorders like bulimia, it is best to consult a doctor for early diagnosis.
Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is important when it comes to bulimia to improve the chances of a good outcome. Diagnosing bulimia can be quite difficult as the individual in question may be in denial or do everything possible to conceal their condition.
Hence, the diagnosis of this disorder is usually aimed at ruling out other possible health conditions. If bulimia is suspected, the concerned individual may be referred to a mental health specialist.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Fifth Edition, the patient must meet the criteria listed below to be diagnosed with bulimia nervosa (5):
- Uncontrollable periods of recurring binge eating.
- Purging after unwanted bingeing by vomiting, fasting, over-exercising, and misusing laxatives and other such drugs.
- The action of bingeing followed by purging has been taking place once a week for the last 3 months.
- The patient’s body shape and weight are influencing his/her feeling of self-worth.
- This behavior is not occurring as a result of anorexia nervosa.
If an individual is diagnosed with bulimia, an apt treatment plan should be put into action immediately. This is because early treatment has been noted to improve the chances of recovery in affected individuals. The following are the most common medical treatments used to combat bulimia.
Treatment Methods
When it comes to bulimia, its treatment is long term. The treatment is often a combination of family therapy, psychotherapy, nutrition counseling, and medications.
Also, it is important for the patient to accept the need for treatment while also agreeing to cooperate and participate in the recovery process.
Treatments may include:
- Behavioral And Cognitive Therapy: To help the patients alter their perception of food, eating, body weight, and appearance. It also aims at helping the patient identify why they are affected by this disorder (6).
- Interpersonal Psychotherapy: To help patients learn new ways to manage conflicts between families and friends (7).
- Nutritional Counseling: To help break the bingeing cycle by teaching the patients how to pace their meals and set calorie goals (8).
- Medications: Fluoxetine (Prozac) is an antidepressant that is often prescribed for managing bulimia (9).
- Support from friends and family is also key to effective and long-term positive outcomes (10).
In rare cases, i.e., when there is a risk of self-harm or suicide, the patient may need to be hospitalized.
The diet of bulimic patients also needs special attention once treatment is completed. With a diet plan already in place, the chances of relapse will be reduced.
Best Diet Plan For Bulimia Nervosa
The diet of bulimic patients must consist of regular meals and snacks. Your dietitian will pay attention to your caloric and nutrient needs while developing a plan.
A typical bulimia recovery plan should include 3 full meals every day in addition to 2 or 3 snacks in between. The meals and snacks will be no longer than 3 hours apart. This is because consuming regular meals has been associated with reduction in binge eating and purging behaviors (11).
Individuals affected by bulimia must follow a balanced diet that consists of protein, starch, vegetables, and fats. Your dietitian may also try to include at least one of your favorite foods in every meal.
It is also recommended that the affected individuals stay away from junk foods like chocolates, ice cream, chips, or any other foods that may trigger binge eating.
The affected individuals also have to make some lifestyle changes to prevent a relapse. The following are some tips that can help.
How To Prevent Bulimia Nervosa
- Avoid caffeinated drinks.
- Quit smoking tobacco.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Stay hydrated by drinking 6 to 8 glasses of water daily.
- Keep your stress under control by practicing yoga or going for a soothing massage.
It may be quite difficult to identify individuals who have bulimia as they may try and conceal their symptoms. Hence, keep a close eye on the suspected individuals – as early diagnosis increases the chances of a good outcome. Also, do the little you can by offering a supporting shoulder to the affected individuals.
For any further queries related to this eating disorder, get in touch with us via the comments below.
Frequently Asked Questions
When to see a doctor for bulimia?
If you or anyone you know are showing symptoms of bulimia, you must get medical help immediately.
What is bulimic behavior?
The individuals may show symptoms of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors like vomiting or using laxatives.
Can bulimia cause hair loss?
Individuals affected by bulimia tend to lose out on important nutrients needed for hair growth. Hence, they may notice increased hair loss.
Which characteristic indicates a binge eating disorder?
Binge eating disorder is characterized by the action of eating large quantities of food in a short span of time, say 2 hours. This action continues until the concerned person feels uncomfortably full.
What is the most accurate statement about women with bulimia nervosa?
The most accurate statement about women with bulimia nervosa would be that they mostly maintain their weight, though there might be slight fluctuations within that range.
How does bulimia affect the body?
Bulimia can affect an individual in a wide range of ways. It messes up one’s appetite, causes weight gain and vitamin deficiencies, and may even result in dehydration and damage to your teeth due to frequent vomiting.
References
- “Bulimia nervosa” BMJ Clinical Evidence, US National Library of Medicine
- “Bulimia Nervosa: A Primary Care Review” Primary Care Companion to The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, US National Library of Medicine
- “The Medical Complications Associated with Purging” International Journal of Eating Disorders, US National Library of Medicine
- “Risk factors across the eating disorders” Psychiatry Research, US National Library of Medicine
- “Characteristics of binge eating disorder in relation to diagnostic criteria” Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, US National Library of Medicine
- “Bulimia Nervosa A Cognitive Therapy Program for Clients” Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, US National Library of Medicine
- “Interpersonal therapy for bulimia nervosa.” Journal of Clinical Psychology, US National Library of Medicine
- “Intensive nutritional counselling in bulimia nervosa: a role for supplementation with fluoxetine?” Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, US National Library of Medicine
- “Fluoxetine as a treatment for bulimia nervosa.” International Journal of Obesity, US National Library of Medicine
- “Family-based therapy for adolescents with bulimia nervosa.” American Journal of Psychotherapy, US National Library of Medicine
- “Meal Patterning in the Treatment of Bulimia Nervosa” Eating Behaviors, US National Library of Medicine

Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our vibrant community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with like-minded individuals.